Ethiopia
Ethiopia confirmed on Monday the deaths of three people who had contracted the Marburg virus. The country’s health ministry said three additional fatalities were being investigated for a possible connection to the disease.
This announcement comes after Ethiopian authorities declared the Marburg outbreak on Friday. The outbreak was reported in the Omo region, an area neighbouring South Sudan.
Ethiopian Health Minister Mekdes Daba said the government had conducted tests in 17 suspected cases in the country's south.
In addition, 129 people who were in contact with the confirmed cases have been isolated and are being monitored.
The minister said there were no active cases but the government was taking preventive measures. A team from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has been dispatched to support with testing and outbreak control.
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus praised the Ethiopian government’s fast action, saying it showed a “commitment to bringing the outbreak under control quickly.”
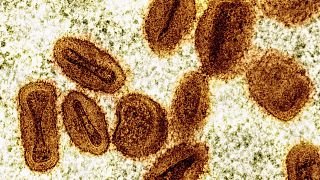
Marburg is a highly contagious haemorrhagic virus from the same family as Ebola.
The Marburg virus originates in fruit bats and spreads between people through close contact with the bodily fluids of infected individuals or with contaminated surfaces, such as soiled bedsheets.
Symptoms include fever, muscle pains, diarrhoea and vomiting. Without treatment, Marburg can be fatal in up to 88% of people who fall ill.
Marburg outbreaks and individual cases have in the past been recorded in Rwanda, Tanzania, Equatorial Guinea, Angola, Congo, Kenya, South Africa, Uganda and Ghana, according to WHO.












00:17
Autopsy shows dead Senegal student suffered multiple traumas
01:05
Madagascar cyclone death toll rises to 59 as devastation mounts
01:00
Zambia closes borders to South African livestock amid FMD outbreak
01:36
Chad: French tourist's death "a tragic accident" according to another traveller
01:13
French tourism group of which one died during visit to leave Chad
00:34
UN rights chief urges Ethiopia and Eritrea to de‑escalate tensions