Ebola virus
The World Health Organization (WHO) has alerted six African countries to watch out for potential cases of Ebola after it emerged in the Democratic Republic of Congo and Guinea.
The DRC declared the emergence of Ebola on February 7 while Guinea declared the outbreak on Sunday.
"We have already alerted the six countries around, including of course Sierra Leone and Liberia, and they are moving very fast to prepare and be ready and to look for any potential infection," the WHO's Margaret Harris told a Geneva briefing.
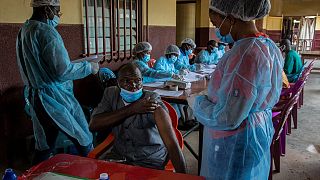
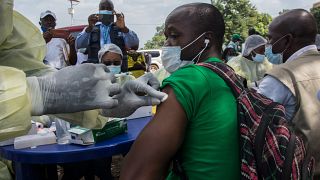
Meanwhile, the Ebola vaccination campaign kicked out Monday in areas where the epidemic was first reported.
Between 2013 and 2016 more than 11,000 people died in the West Africa Ebola epidemic, which began in Guinea.
Ebola infects humans through close contact with infected animals, such as chimpanzees and fruit bats. It then spreads between humans by direct contact with infected blood, fluids, and organs.
It can also be spread indirectly through contact with contaminated environments.











Go to video
South Africa urges effective ceasefire and inclusive dialogue to end DRC conflict
Go to video
Shelters in Burundi overwhelmed as 80,000 flee escalating violence in South Kivu
01:02
Mass layoffs cast shadow over Guinea’s Simandou mega-mine as output begins
01:00
M23 rebels withdraw from Uvira in DRC peace move
Go to video
From Kinshasa to Bujumbura: How the M23 crisis risks engulfing the region
01:00
Videos. Pix of the Day: December 10, 2025